Have you ever wondered how high can your credit score get?
If so, then this article is for you.
First we’ll define the purpose of credit scores. Next we’ll look at the types of scores available. Lastly we’ll discuss why they are important and how to get them to the top of the range.
Credit Reports Versus Credit Scores
Most people get confused when discussing credit reports versus credit scores. They are not the same thing at all.
Your credit report is a summary of your financial history. It lists all the credit cards and loans you’ve applied for over the past 2 years, accounts you’ve opened, your payment history over the last 7 years, your current and previous employers and addresses, and even some public records.
That data is provided by your creditors to the major credit reporting agencies: Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. The credit reporting agencies then compile that data into a report which they sell to lenders and consumers alike. .
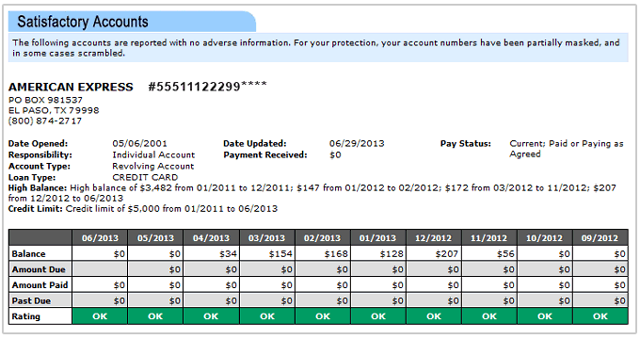
Your credit scores are provided by companies like FICO and Vantage. They run the data listed on your credit reports through some mathematical formulas designed to determine your creditworthiness. The result is demonstrated as a number called a score.
Types of Credit Scores
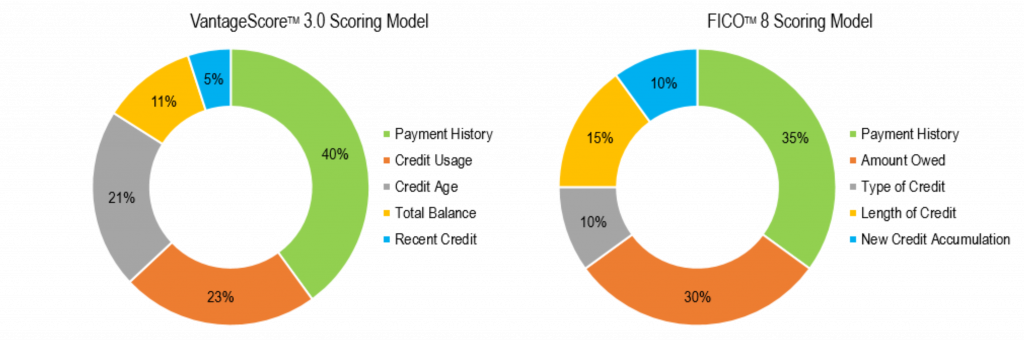
There are two main types of scoring models. They are FICO and Vantage.
FICO was the first effectively marketed credit score used by creditors to make credit decisions.
There are different versions of FICO which are specifically formulated for different industries including mortgage, auto finance, and credit cards.
Each year FICO develops new versions of their credit scores in an attempt to improve their accuracy for predicting creditworthiness.
Vantage is the scoring model created by the 3 major credit reporting agencies. As of 2020 less than 5% of all credit decisions are made using Vantage.
Vantage is the model most often sold to consumers through credit monitoring sites.
Credit Score Ranges
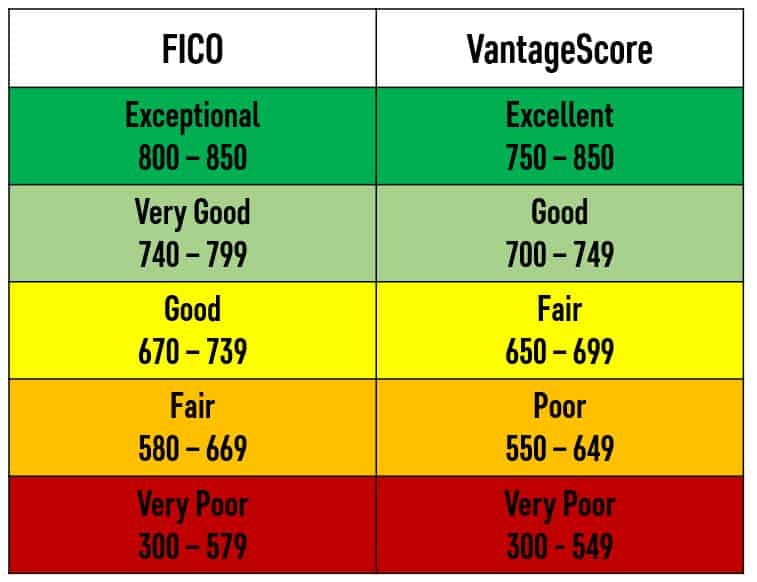
Both credit score models typically use a credit score range of 300-850. However, there are versions of FICO which may go as high as 900.
FICO can only produce a score is the consumer has at least one account active for 6 months or more. VantageScore will produce a score as long as the consumer has at least one active account regardless of age.
In every case, the higher your credit score, the less risk you are to a creditor.
Why Your Score Matters
Credit scores are used to represent your financial responsibility.
A high score signifies that you are a low credit risk and are therefore able to obtain credit and loans at more favorable terms.
A lower score means you are a higher risk of defaulting on your payments to a creditor. This means the creditor will have to charge you more to offset their risk.
The problem with paying more for credit cards, and loans is you have less money left to invest in your education and financial future.
For example, let’s examine how your FICO score might effect your interest rate and monthly payment for a $216,000 home loan repaid over 30 years.
| FICO Score | Interest Rate | Monthly Payment | Total Repayment |
| 740-850 | 3.51% | $972 | $349,920 |
| 700-739 | 3.74% | $998 | $359,280 |
| 680-699 | 3.91% | $1020 | $367,200 |
| 660-679 | 4.13% | $1047 | $376,920 |
| 640-659 | 4.56% | $1102 | $396,720 |
| 620-639 | 5.10% | $1173 | $422,280 |
In this example, by simply increasing your credit scores from 639 to 740 you could potentially save $72,360 in interest payments over the life of the loan.
Properly invested, that money could mean the difference between early retirement or working to make ends meet well into your golden years.
How To Get An 800 Credit Score
First, aim for a score of 750 using the proven steps below:
- Pay your bills on time. Missing just one payment will dramatically lower your scores.
- Keep your balances under 10%. According to MyFICO’s blog, the optimal debt utilization is 6-8%.
- Limit new inquiries to 1 every 6 months. Too many inquiries could indicate you are a credit risk.
- Monitor your credit report for inaccuracies. According to a government accountability study it was estimated that 20% of all consumer credit reports contained serious errors. Check your credit report on a regular basis to give yourself time to correct errors as they occur.
In our experience, the one thing that can push you over the 800 price point is:
- Improve your mix of credit cards and loans. While most people have opened an auto loan, student loan, and mortgage, far fewer have added personal loans. Consider paying off high interest rate debt with a personal loan to improve your ratio of credit to loans.
Conclusion
Although credit scores can go as high as 850 or even 900, there is usually no additional benefit past 740 for most financial products.
A higher credit score can help you get better rates on loans, insurance and other products. Expect to pay higher fees and interest as your rate declines.
Work at improving all 5 factors of your credit score to get it as high as it can go: Payment History, Debt Utilization, Age Of Credit, Mix Of Credit, And New Inquiries.

1 Response to "How High Can Your Credit Score Get?"
[…] to your credit score. Its the presence of the charge off that is keeping you from finding out how high your credit score can get. […]